VSI Regenerative Medicine
Pain Relief
For Neck and Back Pain
We understand the human spine is complex and vital to one’s ability to function. For this reason we have assembled a comprehensive suite of specialties, and employ modern technologies, to provide you with effective solutions not found elsewhere. Our world-renowned team of specialists are here to improve the lives of those suffering from neck and back conditions.
Benefits of
Minimally-Invasive Spine Surgery
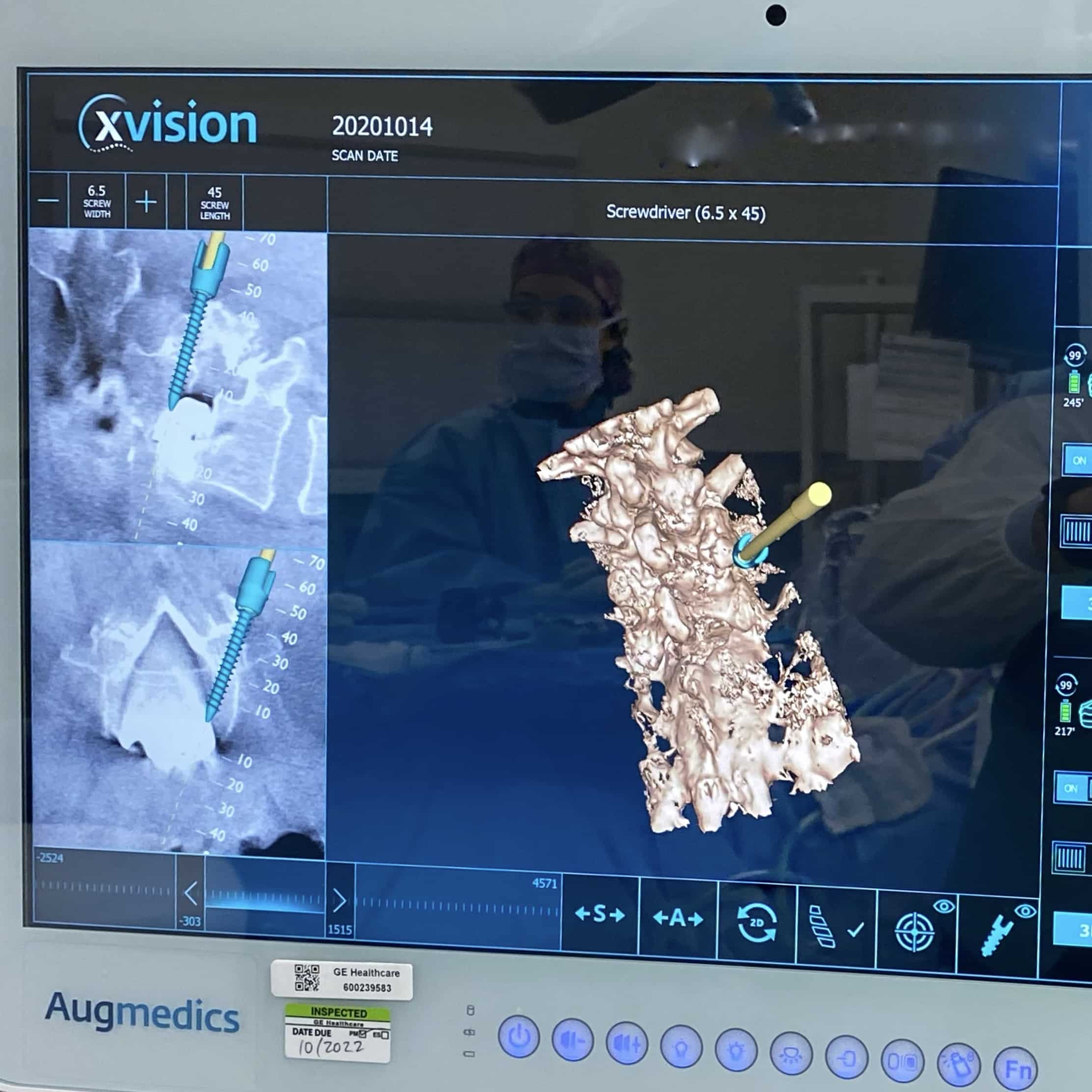
Minimally invasive spine surgery offers the same post-surgical benefits as traditional spine surgery, but with much less trauma. In recent years, minimally invasive techniques have changed the face of spine surgery and ultimately surgical recovery.
Some common benefits associated with non-invasive spine surgery include:
Modern Solutions
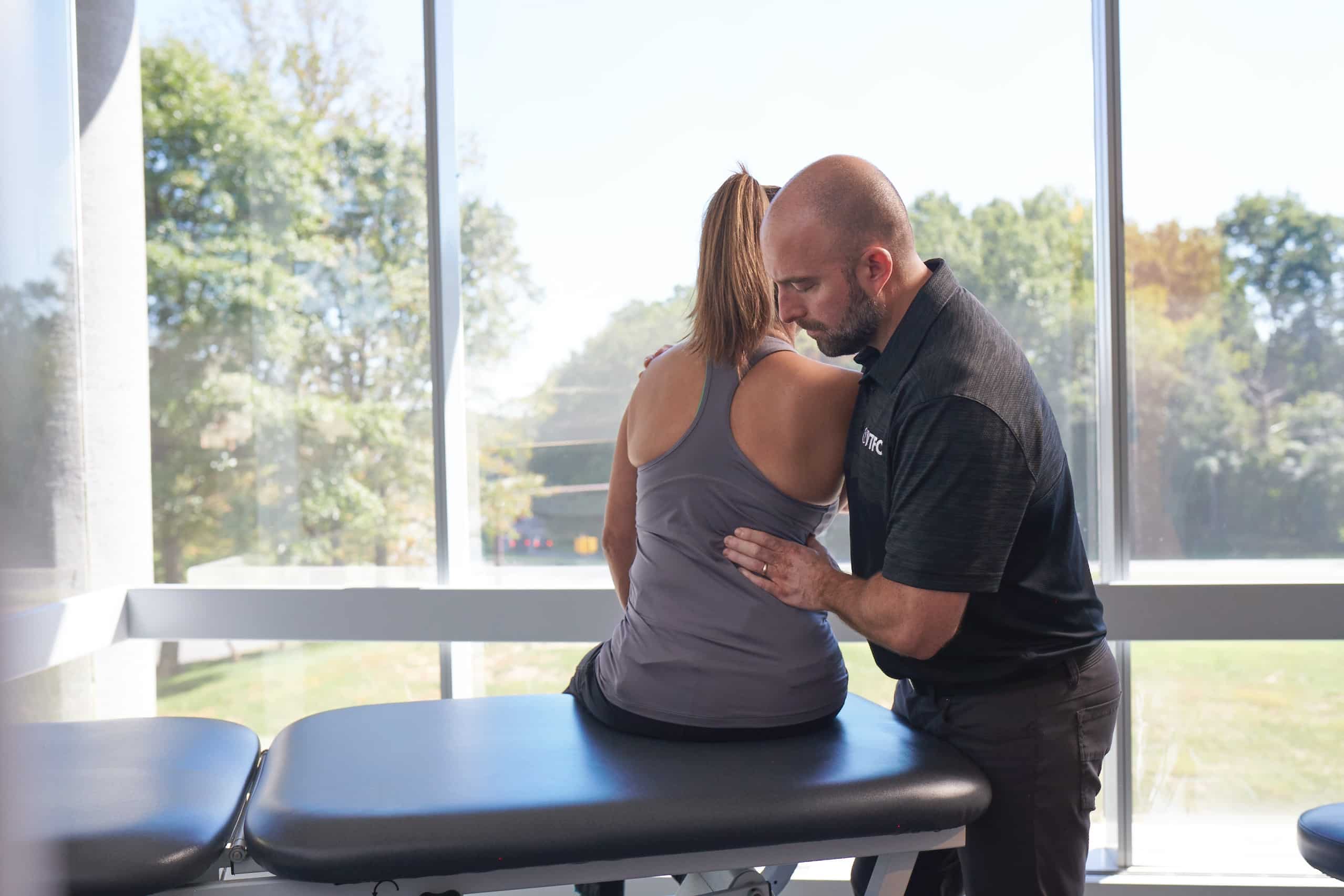
For Non-Operative Care
VSI believes in a multi-disciplinary approach. Our non-surgical team include physical therapists, physiatrists, pain management specialists, and a neurologist. We want our patients to have access to our experts and exemplary care.
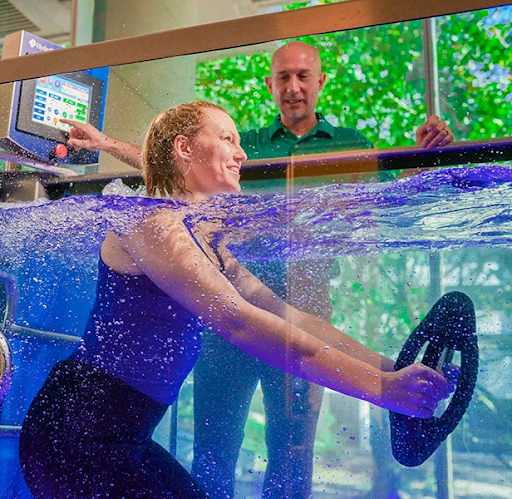


Spine Surgery Recovery
Modernizing the Approach
Our care for our patients doesn’t end in the operating room. This philosophy is unique because we understand the emotional and physical demands surgery may impose. We play an active role in our patients’ recovery by setting expectations and goals so they feel supported through this critical stage of their treatment.