Disc Herniations
Understanding the Symptoms, Causes & Treatments of Disc Herniations
Reviewed by: Dr. Christopher Good, Dr. Colin Haines, Dr. Ehsan Jazini
What is A Herniated Disc?
A disc herniation is a displacement of disc material beyond the normal confines of the disc space. The terms disc protrusion, disc bulge, disc herniation, ruptured disc, and slipped disc all mean the same thing and imply that disc material has left the normal disc space.
The spine is a network of vertebrae that protect the spinal cord. To prevent the bones from rubbing against each other, there are small discs in between them. These discs cushion the bones, while also protecting the nerves as they run through the spinal cord.
If disc material herniates, or squeezes out, this can put pressure on the spinal cord or spinal nerves. This can cause severe pain in the path of the nerve being pinched. Pressure against the nerve root from a herniated disc can cause numbness and weakness along the nerve. When the nerve root is inflamed, the added pressure may also cause vague, deep pain and/or cause sharp, shooting pain to radiate along the pathway of the nerve.
The most common location for a disc herniation to develop is in the lower back (lumbar region of the spine) but can happen in the neck (cervical spine) as well.
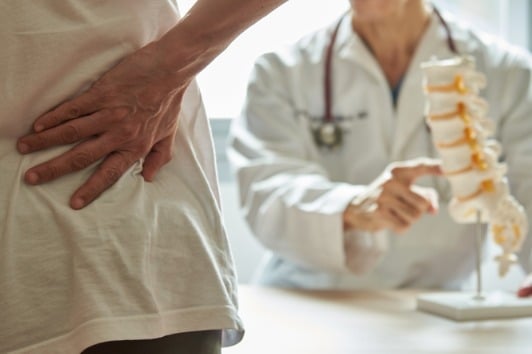
What are Common Symptoms of Herniated Discs?
- You may notice pain that travels down one or both of your arms and legs.
- You may develop numbness and tingling in certain parts of your arms and legs
- You may feel like you are not able to use your arms or legs as much as before
- You may lose your reflexes and certain extremities
- The pain could change depending on your position
Similar to other medical conditions, the symptoms of a herniated disc can change depending on the location and severity of the issue. The slipped disc symptoms depend entirely on the nerves that are impacted, which is dependent on the exact disc that has herniated. That is why it is important to reach out to a professional who can diagnose the issue as quickly as possible.
When Should You Seek Treatment for Disc Herniations?
If you’re noticing symptoms associated with Disc Herniations and suspect a spinal issue, it’s crucial to consider consulting a board-certified spinal specialist. Reach out promptly to a certified spine surgeon for an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. Early intervention can significantly improve your overall well-being and provide a broader range of treatment options, which may decrease as symptoms persist. The key to healing a herniated disc quickly and successfully lies in addressing the root of the pain with your spine specialist as soon as symptoms arise.
While many people experience day-to-day back or neck pain, dismissing it as soreness, this may not be the case for everyone. If your pain persists for more than 10 days, it should be taken more seriously. Evaluate such prolonged pain with a spine surgeon to identify the root issue and determine the appropriate treatment. Additionally, be attentive to other signs related to back or neck pain that should not be ignored, including pain accompanied by fever, pain associated with loss of bladder control, and weakness/tingling/numbness in your arms or legs.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines based on our expertise in spine care over the past three decades, recognizing that each patient’s symptoms may be unique.

What Are Common Causes of Herniated Discs?
There are several possible causes of disc herniation. Some of the most common ones include:
- Bending can place high forces on the discs between each vertebra. If you bend and try to lift a heavy object, the force and stress on your spine can cause a disc to rupture.
- Heavy forces on the neck or low back may simply be too much for even a healthy disc to absorb. For example, falling from a significant height causes a large amount of force through the spine, and if strong enough, a vertebra can break or the disc can rupture.
- A herniated disc can also be a chronic injury, as repeated annular tears can weaken the disc over time.
- If you lift something with a jerking or twisting motion, you could cause a vulnerable disc to herniate.
- The natural process of aging causes discs to become weakened from degeneration.
- Poor posture can also cause herniations. As postural muscles fatigue, excessive tension is placed on the discs, ligaments, and joints.
Ultimately it’s hard to say what specific act can cause a disc to herniate in a patient, but we do know that herniation may occur when too much force is exerted on an otherwise healthy intervertebral disc.
Who is at Higher Risk for Disc Herniations?
There are several risk factors that could make it more likely for you to develop a herniated disc. Some of the most common examples include:
- People who are overweight or obese
- People who have physically demanding jobs that involve a lot of heavy lifting
- People with a family history of disc herniation
- Individuals who smoke are at a markedly increased risk
- While this condition can happen to anyone of any age but are most common in young to middle-aged adults who overwork their body
If you believe that you are at an increased risk of suffering a herniated disc, it is important to reach out to a medical professional. You may be able to reduce your risk of developing the condition by remaining active, stopping smoking, and keeping your weight at a healthy level.

How Are Disc Herniations Diagnosed?
A herniated disc may be diagnosed after a complete history and comprehensive physical exam by a spinal specialist.
Imaging studies are usually a first step in understanding spine pathology. These include:
- Standing and bending X-rays to evaluate spinal alignment, stability and disc space height.
- An MRI is the standard imaging to assess disc and nerve pathology.
- An EMG may be used to determine which specific nerves are involved and the extent of possible nerve damage.
We will work with you to determine whether one or more of these imaging studies is necessary. We want to get a complete picture before we recommend your custom treatment plan.
What are Common Treatments for Herniated Discs?
Pain Medications for Disc Herniations
Herniated disc medications are commonly used to control pain, inflammation, muscle spasm, and sleep disturbance. These may involve steroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), pain medications, and muscle relaxers to help control symptoms and reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy for Herniated Disc
Spine-specialized physical therapy is often prescribed with the goal of assisting in calming pain and inflammation, improving mobility and strength, and helping achieve daily activities with greater ease and ability.
Physical exercises can aid in enhancing the healing process, strengthening the core and spine, improving coordination, and increasing spinal mobility. Specific exercises for herniated discs are particularly beneficial for promoting recovery and relieving discomfort.
Epidural Steroid Injections (ESI)
ESI for herniated discs are usually reserved when other conservative measures do not work, or in an effort to postpone surgery. These injections place a small amount of ‘cortisone’ into the spinal canal. Cortisone is a strong anti-inflammatory medicine that may decrease nerve inflammation and ease pain caused by irritated nerve roots. This treatment is not always successful but may provide short-term help.
When properly identified and treated, most patients will improve with non-surgical care. For the few patients where nerve compression remains too much, minimally invasive surgery is usually highly successful in eliminating the symptoms and allowing people to return to a full and active lifestyle.