Tools For Our Treatments: Robot-Guided Surgery
The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize patient function and accelerate a return to a full life. As spinal surgery has evolved, more focus has been placed on minimizing trauma to the body during surgery and expediting a return to function through the use of minimally invasive techniques. The era of modern spinal surgery has blossomed over the past 15 to 20 years as a result of scientific advancements including minimally invasive surgery, genetic testing, next generation spinal implants, stem cell research, and the use of biologic agents to promote spinal healing. Robot-guided spinal surgery offers many potential advantages to patients and surgeons including improving the safety of both minimally invasive and complex surgical procedures, improving the accuracy of spinal instrumentation placement, and minimizing the use of radiation during surgery. Robot-guided spine surgery utilizes highly accurate, state-of-the-art technology for the treatment of many spinal conditions including degenerative spinal conditions, spine tumors, and spinal deformities.
How It Works:
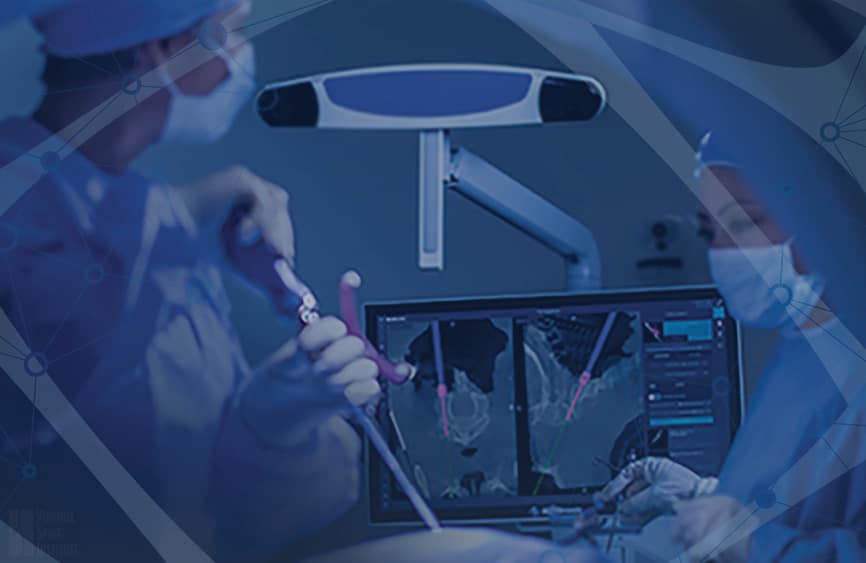
The Mazor Robotics’ Renaissance system is one of the only robotic guidance products in the United States used for implanting devices during spine surgery. The Mazor Robotics system allows the surgeon to use the images from a computerized tomography scan (CT scan) that is taken before surgery to create a blueprint for each surgical case. The CT scan information is loaded into a computerized 3D planning system which allows the surgeon to plan the surgical procedure with a high degree of precision before ever entering the operating room. In the operating room, the surgeon does all of the physical work of the surgery. The robot-guidance sys-tem is a tool that helps to guide the surgeon’s instruments based on the highly accurate pre-operative planning of spinal implant placement. During the surgery, the robot is placed near the patient either by attaching it to the bed or directly anchoring it to the spine of the patient. The robot is approximately the size of a 12 oz. beverage can with a small arm attached. The robot has the ability to bend and rotate in order to place its arm on the spine in a very specific location and trajectory. This ultra-precise guidance can improve the surgeon’s ability to safely place implants, particularly when working through very small incisions (minimally invasive surgery) or when dealing with complex anatomy (spinal deformity or previous spine surgery).
Robots & Minimally Invasive Spine Fusion:
One common technique presently used by spine surgeons to correct spinal conditions is spine fusion. The purpose of a spinal fusion is to create a rigid union between two separate segments of the spine to correct malalignment or instability. Spine fusion has traditionally been performed using “open surgery” with an incision that is big enough to expose the entire area being treated. Open surgical techniques are beneficial and necessary for many conditions; however, in some cases minimally invasive surgery (MIS) can be utilized to safely obtain a similar result. MIS uses smaller incisions which usually result in less damage to surrounding healthy tissue, less post-operative pain, and faster recovery. In many situations, MIS requires an increase in the use of intraoperative x-rays in order to compensate for a surgeon’s inability to directly visualize the spine. In some cases, this lack of visualization could decrease the surgeon’s accuracy when compared to open surgery. In addition, the increased radiation exposure during surgery is a concern for the patient as well as the health care team, as previous studies have shown an increased rate of cancer among spine surgeons, compared to the general population. Robot-guided surgery technology allows the surgeon to perform MIS in a very precise fashion while minimizing the need for radiation during the surgical procedure. Robot-guidance technology guides the surgeon’s tools during MIS to ensure accuracy while also decreasing tissue trauma, resulting in less bleeding, smaller scars, less pain, and faster recovery.
location of spinal implants is blueprinted with 3D software. The orange and purple lines represent screws that are to be placed into the bones of the spine.
Robot-guided spine surgery is a promising new technology that has many advantages and may allow surgeons to perform less invasive surgical procedures with smaller incisions, less bleeding, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays. Robot-guidance also can increase the accuracy and safety of surgical procedures and allow these procedures to be performed with less intra-operative radiation exposure to patients and health care providers.
Topics covered
About the Author
Featured Resources
Insights to Achieve a Pain-Free Life